📌 Core Idea Overview
| Concept | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Infinite Geometric Sequence | A geometric sequence that continues endlessly, where each term is formed by multiplying the previous term by a constant ratio r. |
| Condition for a Finite Sum | The total sum only exists when the absolute value of the common ratio is less than 1, meaning the terms become progressively smaller. |
| Sum Formula | The sum of an infinite geometric sequence is S = a ÷ (1 − r), where a is the first term and r is the common ratio. |
📌 Understanding Infinite Geometric Sums
- An infinite geometric sequence is formed when a sequence follows the pattern: a, ar, ar², ar³, and continues without stopping.
- Although the sequence has infinitely many terms, its total sum can be finite if each term gets smaller rapidly enough.
- This happens only when the common ratio r satisfies −1 < r < 1, ensuring that each new term contributes less to the total sum.
- If |r| ≥ 1, the sequence either grows without bound or oscillates without settling, and therefore no finite sum exists.
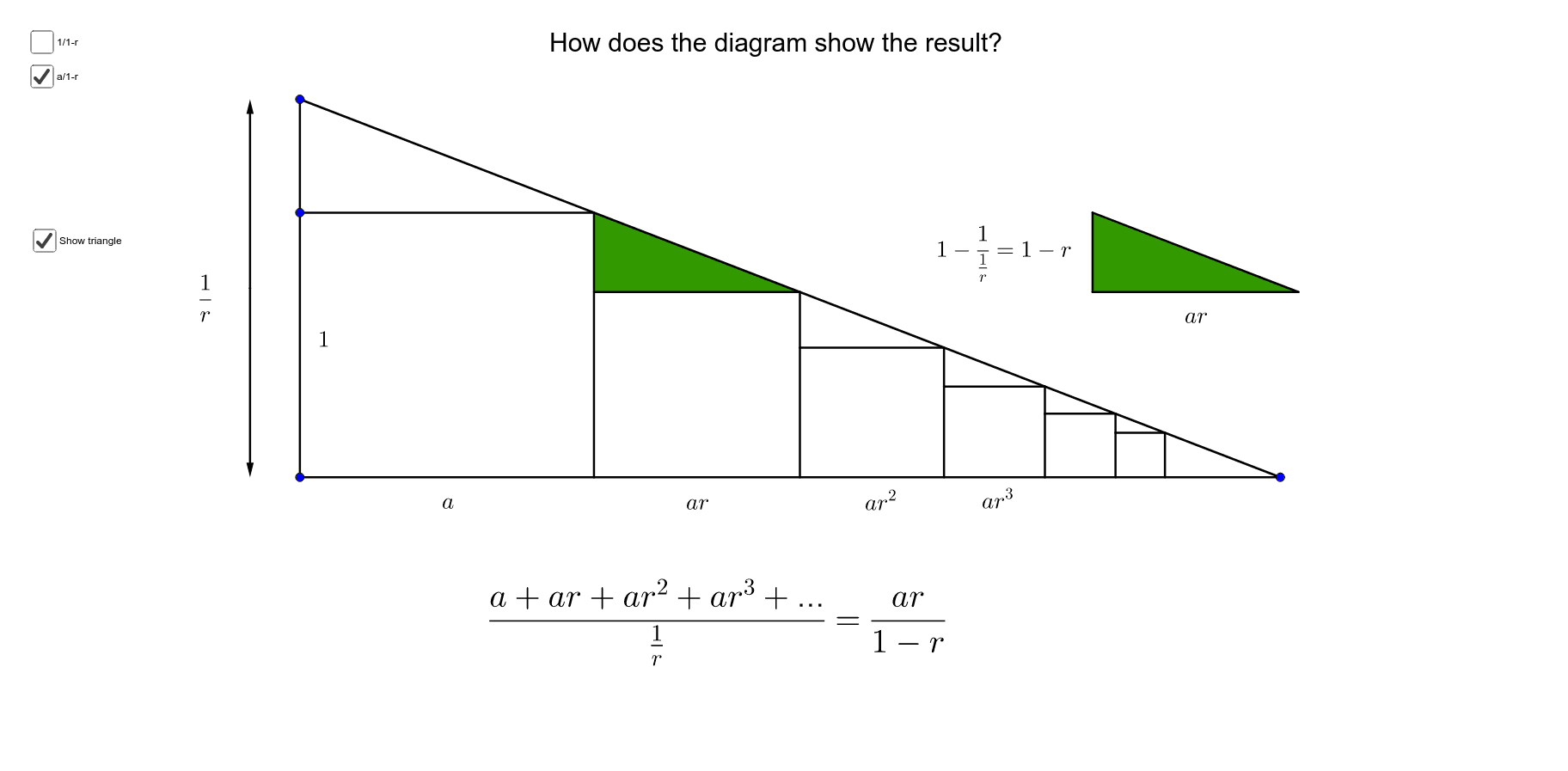
📌 Formula for the Sum of an Infinite Geometric Series
- The sum S of an infinite geometric sequence is given by: S = a / (1 − r).
- a represents the first term of the sequence.
- r is the common ratio between successive terms.
- This formula is derived using the idea of limits, where the partial sums approach a fixed value as the number of terms increases.
material-mGcA23AB.png
📌 Worked Example
Example: Find the sum of the infinite geometric sequence 6 + 3 + 1.5 + …
- The first term a = 6.
- The common ratio r = 3 / 6 = 0.5.
- Since |r| = 0.5 < 1, the infinite sum exists.
- Apply the formula: S = 6 / (1 − 0.5).
- S = 6 / 0.5 = 12.
🧠 Examiner Tip:
Always check that the absolute value of the common ratio is less than 1 before applying the infinite sum formula.
Many students lose marks by applying the formula when |r| ≥ 1, where the sum does not exist.
Always check that the absolute value of the common ratio is less than 1 before applying the infinite sum formula.
Many students lose marks by applying the formula when |r| ≥ 1, where the sum does not exist.
🔍 TOK Perspective:
Infinite geometric sums rely on the idea of infinity, which cannot be directly experienced in the physical world.
Yet mathematics treats infinity as something that can be manipulated precisely.
This raises deep questions about whether mathematical knowledge is discovered or constructed by human reasoning.
Infinite geometric sums rely on the idea of infinity, which cannot be directly experienced in the physical world.
Yet mathematics treats infinity as something that can be manipulated precisely.
This raises deep questions about whether mathematical knowledge is discovered or constructed by human reasoning.
🌍 Real-World Connection:
The total distance travelled by a bouncing ball can be modeled using an infinite geometric series.
Each bounce covers a fixed fraction of the previous height, forming a decreasing geometric pattern whose total distance converges to a finite value, even though the bouncing continues indefinitely.
The total distance travelled by a bouncing ball can be modeled using an infinite geometric series.
Each bounce covers a fixed fraction of the previous height, forming a decreasing geometric pattern whose total distance converges to a finite value, even though the bouncing continues indefinitely.