A1.1.3 – ORIGIN OF WATER ON EARTH
📌 Definition Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Asteroid Hypothesis | A theory suggesting Earth’s water came from asteroid or meteorite impacts. |
| Carbonaceous Chondrites | A type of meteorite believed to contain ice and organic compounds. |
| Goldilocks Zone | The region around a star where temperatures are just right for liquid water. |
| Exoplanet | A planet that exists outside our solar system. |
| Water Signature | Evidence of water vapor or liquid in a planet’s atmosphere. |
| Transit Spectroscopy | A method for detecting atmospheric composition of exoplanets using light. |
📌 Introduction
Understanding the origin of water on Earth is vital to understanding how life began. This topic explores how water may have arrived from extraterrestrial sources, why water is central to the emergence of life, and how we use this knowledge in the search for life beyond Earth. It also explains key scientific methods used in modern astrobiology.
📌 Origin of Water on Earth
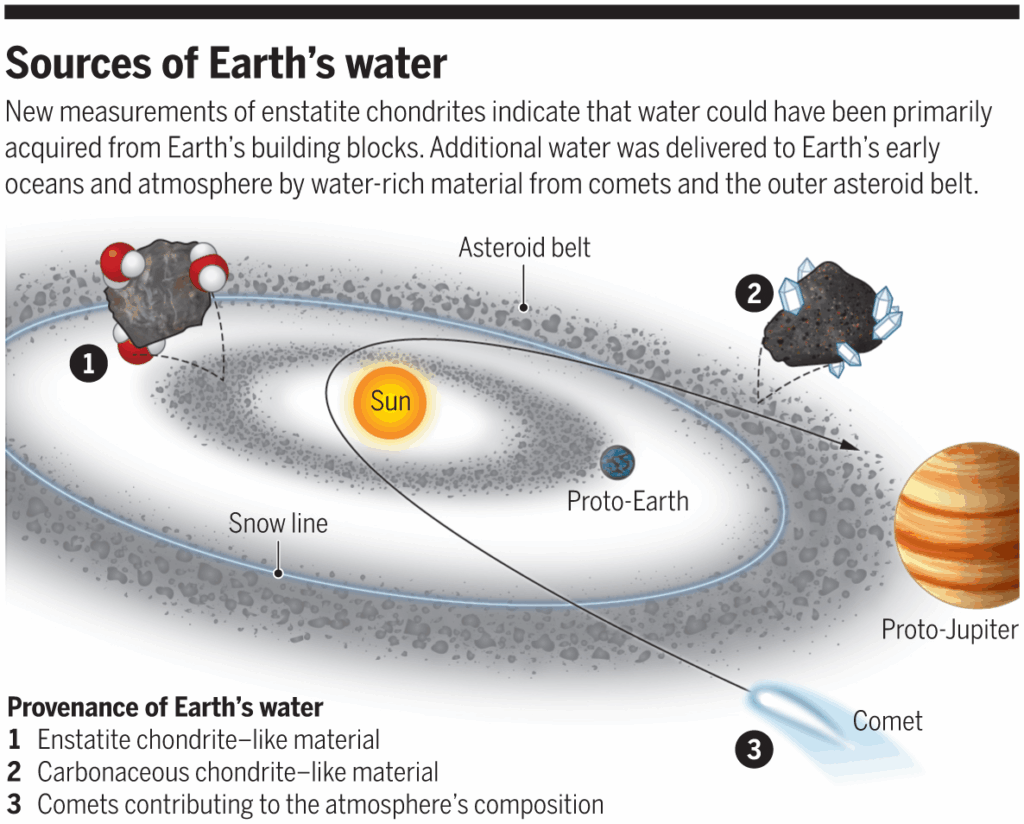
- Earth was initially too hot to retain water, so early oceans could not form directly.
- The asteroid hypothesis suggests water came from space, via icy meteorites colliding with Earth.
- Carbonaceous chondrites are ancient meteorites that contain water and organic molecules.
- These meteorites have hydrogen isotopes similar to those found in Earth’s oceans.
- Another group, eucrite achondrites, also matches Earth’s hydrogen isotope ratio.
- Water released by these impacts could condense into liquid once Earth cooled, forming oceans.
🧠 Examiner Tip: Focus on carbonaceous chondrites, hydrogen isotopes, and the link to early oceans. You only need to study the asteroid hypothesis for IB exams.
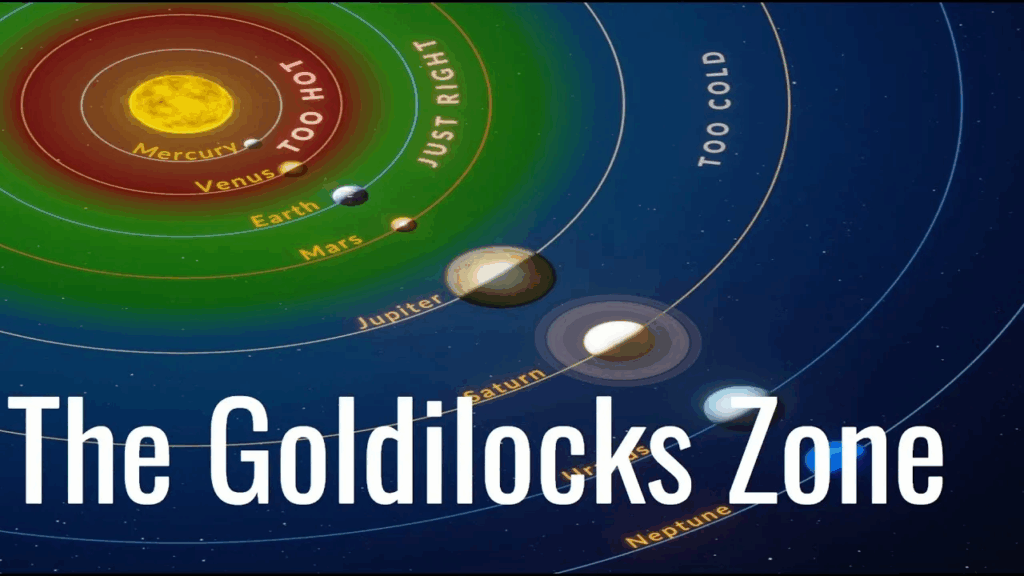
📌 Conditions for Liquid Water and Life
- Liquid water can only exist if a planet is not too hot or too cold.
- The Goldilocks zone is the habitable region around a star where water stays liquid.
- Earth is in the Sun’s Goldilocks zone, enabling stable bodies of water to form.
- Water’s unique properties (solvent ability, heat stability) support complex life.
- All known life forms require water for metabolism, structure, and reproduction.
- The search for extraterrestrial life focuses heavily on planets that may contain water.
⚗️ IA Tips & Guidance: While you can’t test exoplanets in a lab, you can design IAs modeling planetary habitability, water properties, or temperature effects on phase change — always link back to life-supporting conditions.
📌 Search for Life: Water as an Indicator
- Scientists look for exoplanets located in the Goldilocks zone of their solar systems.
- To assess habitability, they use transit spectroscopy — studying how light filters through a planet’s atmosphere.
- If water vapor is detected, the planet is said to have a water signature.
- Planets also need to be massive enough to retain an atmosphere that can support liquid water.
- A water signature does not confirm life but suggests favorable conditions.
- Combined with other markers (e.g., oxygen, methane), it increases the chance of life being possible.
🔍 TOK Perspective: How reliable is water as an indicator of life? Are we limited by anthropocentric bias in assuming that all life must be water-based?
📌 Role of Water in Life’s Emergence
- Life is believed to have originated in aqueous environments like hydrothermal vents.
- Water allowed solutes to dissolve, react, and be contained within membrane-bound structures.
- These early protocells could carry out basic metabolic reactions inside water.
- Water’s thermal stability allowed life to evolve in stable, buffered environments.
- Many theories suggest water was essential in protein folding and replication mechanisms.
- Life’s dependency on water is still seen today — all cells require water to function.
❤️ CAS Link: Create a campaign or workshop educating others on why Earth’s water is rare and valuable, linking space science with sustainability.
🌍 Real-World Connection: Missions like NASA’s Kepler and James Webb telescopes aim to detect water on exoplanets, informing both space exploration and environmental ethics here on Earth.