B2.2.2 – ADAPTATIONS OF MITOCHONDRIA AND CHLOROPLASTS
📌Definition Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cristae | Folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane that increase surface area for ATP production. |
| Matrix | Fluid-filled space inside mitochondria containing enzymes, ribosomes, and mitochondrial DNA. |
| Thylakoid | Flattened membrane-bound sac in chloroplasts where light-dependent reactions occur. |
| Stroma | Fluid-filled space in chloroplasts containing enzymes, ribosomes, and DNA. |
| Photosystem | Protein-pigment complex in thylakoid membranes that captures light energy. |
📌Introduction
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are double-membrane organelles responsible for ATP production through respiration and photosynthesis respectively. Their structures are highly adapted to maximise efficiency in energy conversion.
❤️ CAS Link: Create an interactive 3D model of mitochondria and chloroplasts for a school science fair, explaining how each adaptation aids energy production.
📌 Structure and Adaptations of Mitochondria
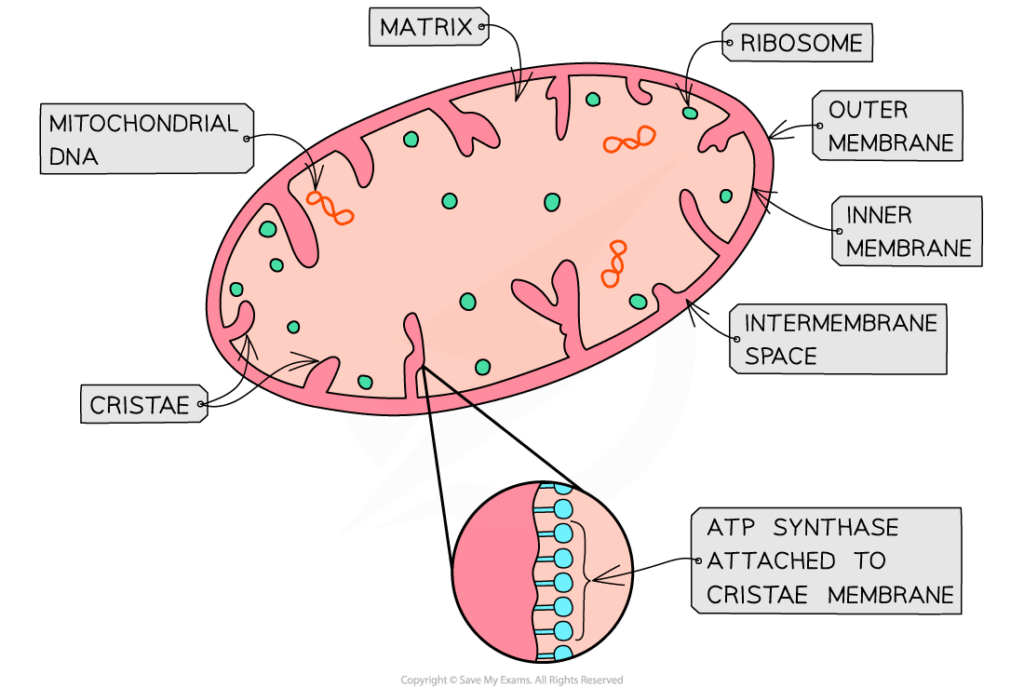
- Double membrane: Outer membrane allows molecule entry; inner membrane is highly selective and folded into cristae.
- Cristae: Increase surface area for the electron transport chain and ATP synthase.
- Matrix: Contains enzymes for the Krebs cycle, ribosomes for protein synthesis, and mitochondrial DNA for enzyme production.
- Intermembrane space: Allows accumulation of protons for chemiosmosis.
- Small size: Increases surface area-to-volume ratio for faster diffusion of substrates and products.
- Dynamic nature: Can change shape and number to meet cell energy demands.
🧠 Examiner Tip: Always link the structure of cristae to increased ATP production capacity in mitochondria-related questions.
📌 Structure and Adaptations of Chloroplasts
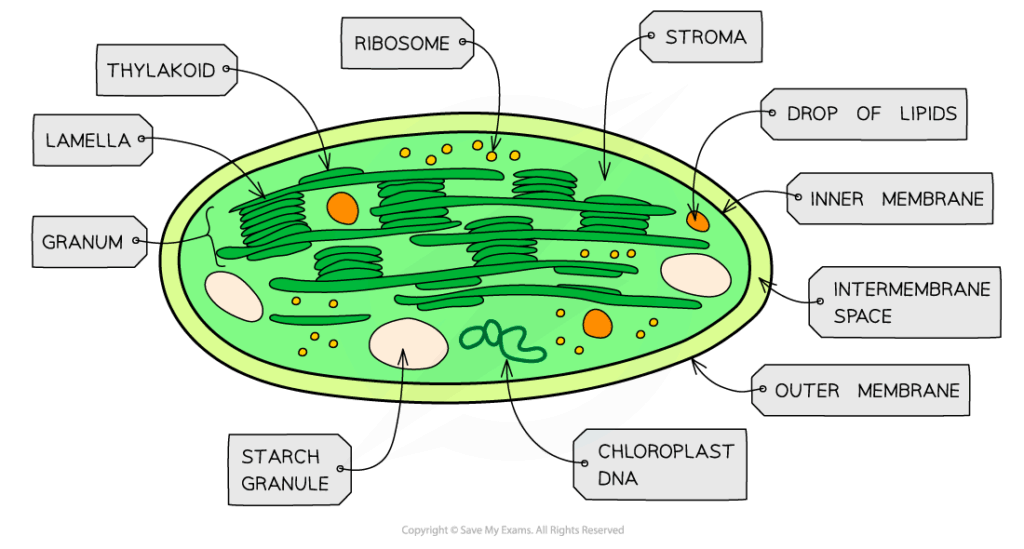
- Double membrane: Controls exchange of substances with cytoplasm.
- Thylakoids: Contain photosystems, electron carriers, and ATP synthase for the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis.
- Grana: Stacks of thylakoids increase surface area for light absorption.
- Stroma: Contains enzymes for the Calvin cycle, ribosomes, and chloroplast DNA.
- Pigments: Chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids absorb different wavelengths of light.
- Interconnected thylakoid membranes: Efficient transport of energy and products between light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
🌍 Real-World Connection: Chloroplast adaptation research has been used in developing high-efficiency crop plants through genetic modification.
📌 Shared Features of Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
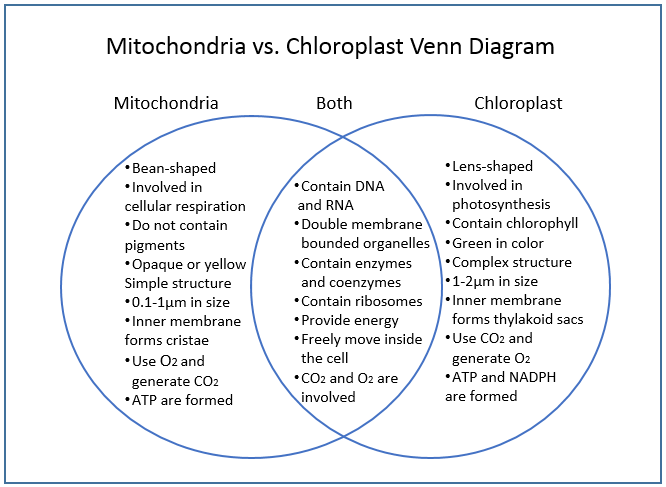
- Both have double membranes, DNA, and 70S ribosomes — enabling production of some proteins independently of the nucleus.
- Both generate ATP through chemiosmosis using electron transport chains.
- Both maintain proton gradients across internal membranes.
- Endosymbiotic theory explains their origin from free-living prokaryotes.
- Presence of multiple copies of DNA and ribosomes allows rapid synthesis of proteins for energy conversion.
🔍 TOK Perspective: The acceptance of the endosymbiotic theory shows how competing hypotheses can exist until technological advances (e.g., DNA sequencing) provide conclusive evidence.
🌐 EE Focus: An EE could investigate variations in chloroplast density between sun and shade leaves using microscopy and image analysis software.