S2.1 The Ionic Model
S2.1.1 and S2.1.2 – The Ionic Bond
📌 Ions :
- Metals are electropositive in nature, as they tend to lose electrons
- Metals have low effective nuclear charges and low ionization energies, making it easy for them to lose electrons
- When a metal atom loses electrons, it forms a positive ion called a cation
- Non metals are electronegative in nature, as they tend to gain electrons
- Non metals have high effective nuclear charges and can attract the transferred electrons strongly
- When a non metal atom gains electrons, it forms a negative ion called an anion
- The number of electrons lost/gained depend on the electronic configuration of the element
- Transition metals can form more than 1 ion and show a range of oxidation states because they do not usually have fully filled outer shells
- The most rigorous reactions occur between elements that are farthest apart on the periodic table
⭐️ Caesium Fluoride (CsF) is considered the most ionic compound.
- The attraction between ions increases with ionic charge but removing multiple electrons has an energy cost
- High ionization energies of metals prohibit electron loss from inner shells, preventing them from attaining higher ionic charges
- Addition of multiple ions makes negative ions more attractive, but addition becomes increasingly difficult due to electron-electron repulsions
⭐️ The formation of Si4- is not feasible for this reason.
📌 The Ionic Bond :
- When an ionic compound is formed, electrons are transferred from the electropositive atom to the electronegative atom to form cations and anions
Eg. Lewis Dot and Cross Structure of NaCl
⭐️ Ionic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
📌 Naming Ionic Compounds :
- Systematic names of compounds use oxidation numbers – only necessary when element shows more than one common oxidation state
| Formula of compound | Oxidation State | Systematic Name |
| FeO | +2 | iron (II) oxide |
| Fe2O3 | +3 | iron (III) oxide |
- Named with cation followed by anion
- No net loss/gain of electrons : deducing formula involves balancing the total number of positive and negative charges
- Polyatomic ions are made up of more than one atom which together have lost or gained an electron
📌 Common polyatomic ions to know :
| Polyatomic ion name | Formula |
| nitrate | NO3 – |
| sulfate | SO4 2- |
| phosphate | PO43- |
| hydroxide | OH– |
| hydrogencarbonate | HCO3– |
| carbonate | CO32- |
| ammonium | NH4+ |
🧠 While bonding between the polyatomic ion and the other ion is ionic, bonding within the polyatomic ion remains covalent.
S2.1.3 Ionic Structure and Properties :
📌 Physical Properties of Ionic Compounds :
- Many cations and anions arrange themselves in a characteristic lattice structure
- no individual molecules
- all positive ions attract negative ions
- bonding is uniform
- Fixed arrangement of repeating units called a formula unit (ratios of ions present)
🧠 Make sure you avoid the term ‘molecule’ while describing an ionic compound and instead use the term ‘formula unit’
⭐️ Coordination number represents the number of ions that surround a given ion in a lattice
⭐️ Lattice enthalpy is the energy required to break 1 mol of ionic solid into its constituent gaseous ions
- Lattice enthalpy as a measure of the strength of ionic bonding
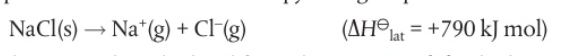
📌 Calculating lattice enthalpy using the ionic model :
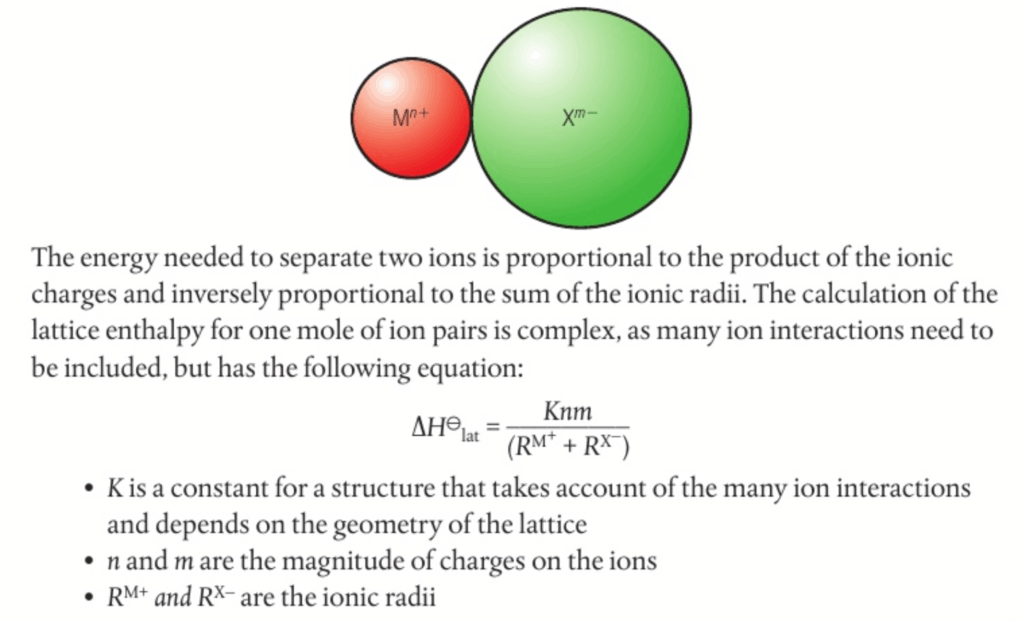
- Increase in ionic charge increases ionic attraction and lattice enthalpy
- Increase in radius of one of the ions decreases ionic attraction and lattice enthalpy
- Lattice enthalpy is greater for smaller ions with a larger charge density
- Melting and Boiling points
- High melting and boiling points
- Crystalline solids at room temperature
- Large amount of energy required to overcome the strong electrostatic forces
- Volatility
- ⭐️ How readily a substance vaporizes
- Ionic compounds have low volatility
- Solubility in water
- Soluble in water as it is a polar solvent
- Energy released when ions are surrounded by water (ion-dipole) pays back energy required to overcome lattice
- Solubility in non polar solvents
- Not soluble in non polar solvents
- Weak interactions (LDF) would not pay back lattice enthalpy
- Electrical conductivity
- ⭐️ Conductivity is the flow of charged particles
- Ionic compounds do not conduct when solid as the ions are not free to move
- Conduct electricity when molten
- Conduct electricity when dissolved in water
- Ionic compounds are generally brittle – crystals tend to shatter when shear force is applied
- Ionic character can be calculated using difference in electronegativities
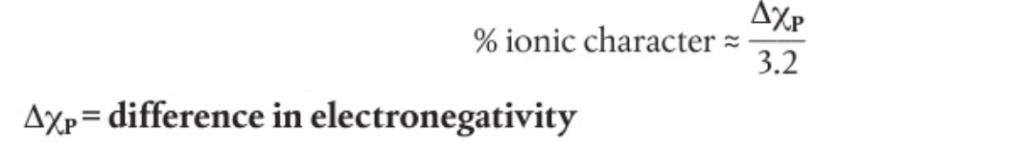
⭐️ CsF is considered 100% ionic with a difference of 3.2.
⭐️ Ionic compounds >1.8 on the Pauling scale