A4.1.1 – EVOLUTION AND EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
📌Definition Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Evolution | Changes in the heritable characteristics of organisms over generations. |
| Natural Selection | Process where advantageous traits become more common because they improve survival and reproduction. |
| Heritable Characteristics | Traits determined by alleles that can be passed to offspring. |
| Mutation | Random change in DNA sequence that may produce new alleles. |
| Homologous Structures | Structures with similar underlying anatomy but different functions, indicating shared ancestry. |
| Analogous Structures | Structures with similar function but different evolutionary origins, arising from convergent evolution. |
| Artificial Selection | Human-directed breeding to enhance desirable traits; also called selective breeding. |
| Molecular Evidence | DNA, RNA, or protein sequence comparisons used to determine evolutionary relationships. |
📌Introduction
Evolution explains the diversity of life on Earth as species change over time through genetic variation and natural selection. Evidence from molecular biology, comparative anatomy, selective breeding, and fossil records supports the theory. While Darwin’s natural selection remains the central explanation, modern molecular data have refined our understanding of how species evolve and adapt.
❤️ CAS Link: Collaborate with a local science museum to create an educational exhibit explaining how molecular evidence and anatomy support evolution.
📌 Darwinian vs. Lamarckian Evolution

- Darwin’s Theory: Variation exists within populations due to random mutations. Individuals with advantageous traits survive and reproduce more successfully, passing those traits on. Over time, these traits become more common.
- Lamarck’s Theory: Suggested traits acquired during an organism’s lifetime (e.g., stretched giraffe neck) could be inherited. This has been disproven except for limited epigenetic influences.
- Darwin’s theory requires heritability; Lamarck’s does not.
- Modern evidence strongly supports Darwin’s model, with minor updates such as recognising that evolution can sometimes occur rapidly (e.g., antibiotic resistance).
🧠 Examiner Tip: In Paper 2, contrast mechanism and heritability when comparing Darwin and Lamarck.
📌 Molecular Evidence for Evolution
- Sequence data from DNA, RNA, and proteins allow scientists to compare species.
- More similarities in sequences indicate closer evolutionary relationships.
- Conserved sequences (e.g., haemoglobin genes) are used because they change slowly and are found across many species.
- Example: Humans and chimpanzees share ~99% DNA sequence identity, indicating recent common ancestry.
- Data from multiple genes increases certainty and can be used to construct evolutionary trees.
🌍 Real-World Connection: Genomic comparisons are used to track zoonotic disease origins, like tracing SARS-CoV-2 back to coronaviruses in bats.
📌 Artificial Selection (Selective Breeding)
- Humans breed organisms with desirable traits over many generations.
- Works faster than natural selection because humans control which individuals reproduce.
- Examples:
- Cows bred for higher milk yield.
- Crops bred for disease resistance.
- Demonstrates evolution in action by showing how heritable changes accumulate over time.
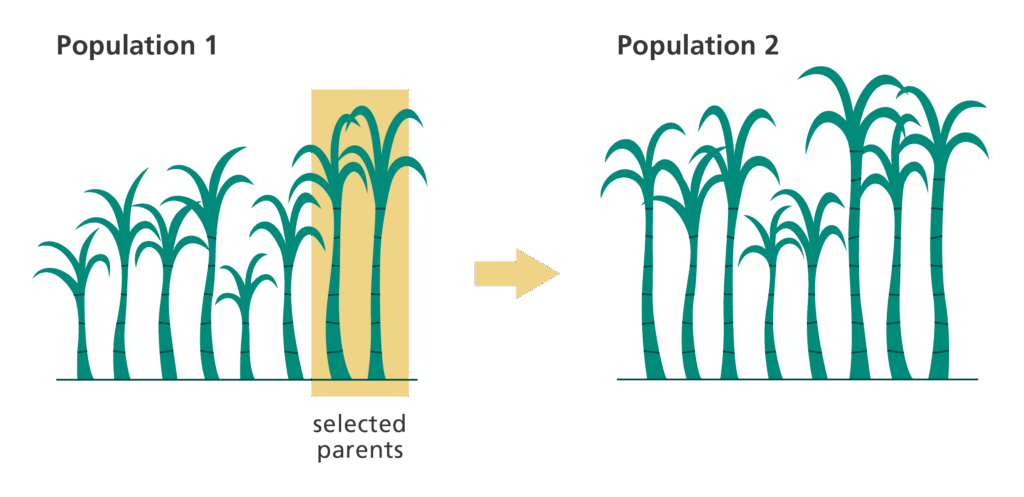
🔍 TOK Perspective: Selective breeding reflects human-driven evolution — raises questions about ethics and long-term ecological impacts.
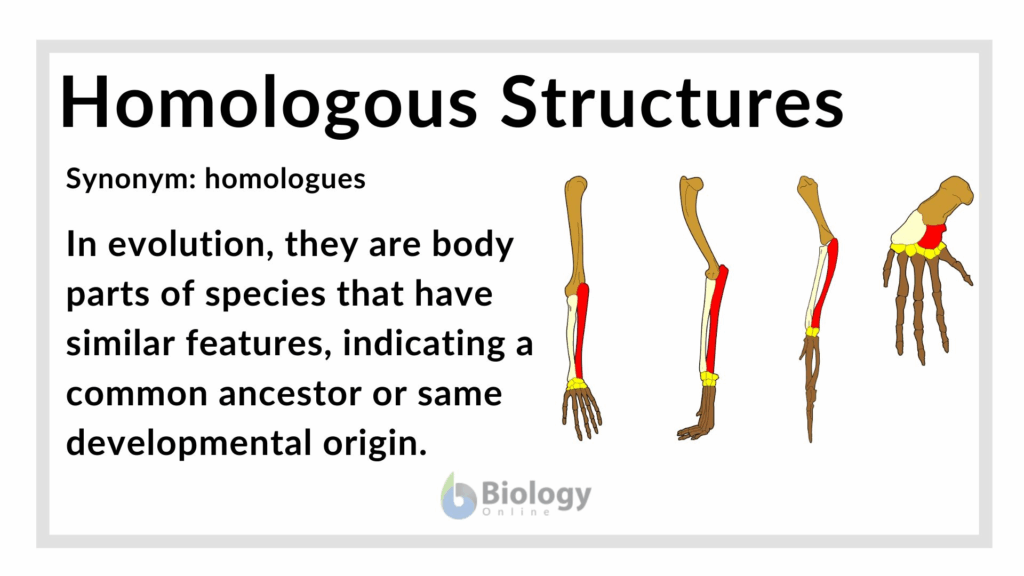
📌 Homologous Structures
- Structures with similar anatomy but adapted for different functions.
- Example: The pentadactyl limb in humans, whales, birds, frogs, and alligators has the same bone layout but is adapted for walking, swimming, flying, or jumping.
- Supports adaptive radiation — species evolved from a common ancestor but adapted to different environments.
📝 Paper 2 Tip: Use function + structure when explaining homologous structures.
📌 Convergent Evolution and Analogous Structures
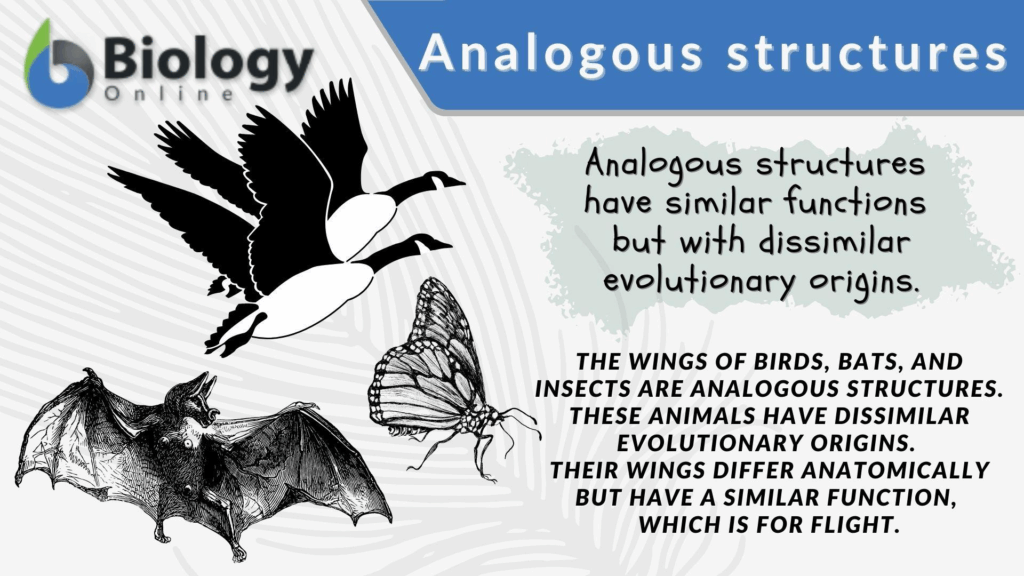
- Analogous structures have similar functions but different evolutionary origins.
- Result from convergent evolution — unrelated species evolve similar traits due to similar selection pressures.
- Examples:
- Streamlined bodies in dolphins (mammals) and sharks (fish).
- Spiny, water-storing stems in cacti (Americas) and euphorbia (Africa).
- Shows that similar environments can shape unrelated species in similar ways.
🌐 EE Focus: An EE could investigate morphological convergence in desert plants using phylogenetic methods.