A2.1.3 – EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION OF LIFE
📌Definition Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| LUCA | Last Universal Common Ancestor — the most recent organism from which all life descends. |
| Hydrothermal Vent Hypothesis | Theory that life evolved around deep-sea vents with rich chemical environments. |
| Molecular Clock | Technique using mutation rates to estimate divergence times between species. |
| Autotroph | An organism that produces its own food from inorganic sources. |
| Fossil Record | Preserved remains or traces of ancient life used to study evolutionary history. |
| Radiometric Dating | Method for determining the age of rocks/fossils using decay of radioactive isotopes. |
📌Introduction
Evidence for the evolution of life combines molecular biology, geology, and paleontology. DNA and protein comparisons reveal shared ancestry, while fossils and dating techniques establish timelines for life’s emergence. Geological evidence suggests life may have originated in extreme environments, such as hydrothermal vents, where chemical energy supported early organisms.
❤️ CAS Link: Create an interactive school exhibit showing models of hydrothermal vents and extremophile habitats.
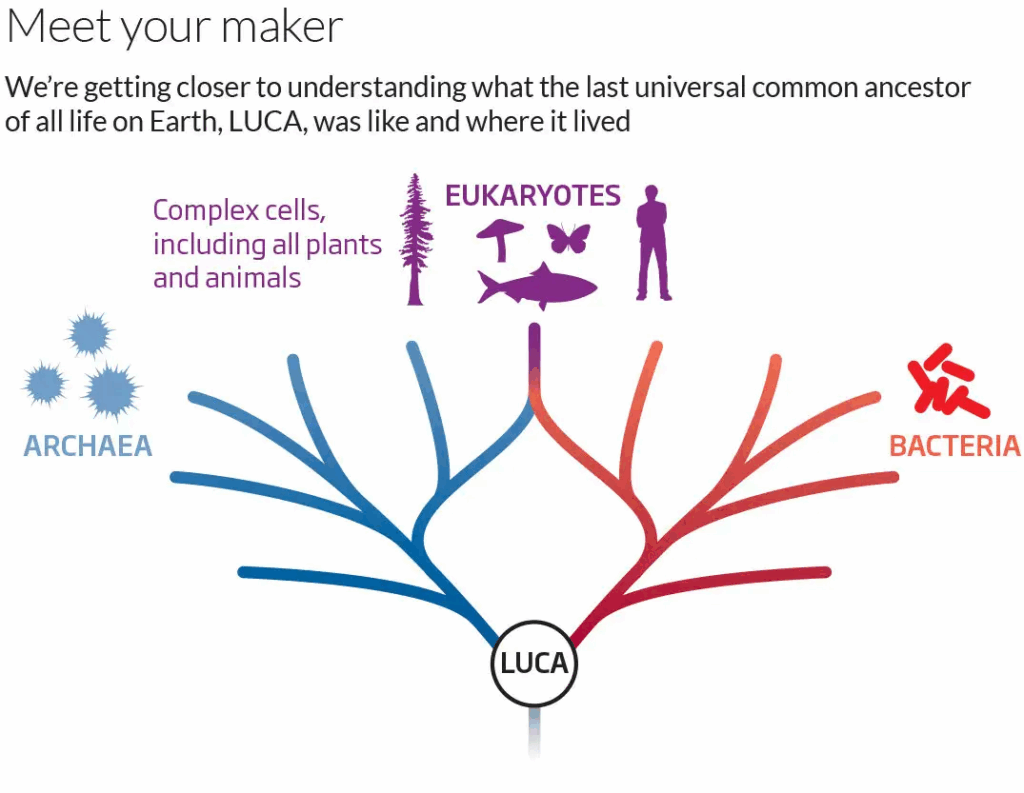
📌 Molecular Evidence for Common Ancestry
- All living organisms share the same genetic code, supporting a common origin.
- DNA sequences and protein structures show strong similarities across species.
- Universality of basic biochemical pathways (glycolysis, ATP synthesis) points to a shared ancestor.
- Molecular clock analysis uses mutation rates to estimate divergence times.
- Similarity in ribosomal RNA sequences is a strong evolutionary marker.
- LUCA likely had a simple but fully functioning genetic and metabolic system.
🧠 Examiner Tip: In “evidence” questions, include molecular, structural, and biochemical similarities — not just DNA sequences.
📌 Geological and Fossil Evidence
- The oldest known microfossils date to around 3.5 billion years ago.
- Stromatolites, layered structures from microbial mats, provide early evidence of life.
- Fossils are dated using radiometric methods such as uranium–lead or potassium–argon dating.
- Sedimentary rock layers help reconstruct the sequence of evolutionary events.
- Fossil evidence is limited due to the rarity of preservation and erosion over time.
- Isotopic signatures in ancient rocks suggest biological carbon fixation occurred early in Earth’s history.
🌍 Real-World Connection: Fossil dating techniques are also applied in archaeology to date ancient human remains and artefacts.
📌 Hydrothermal Vent Hypothesis

- Proposes that LUCA evolved in deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
- Vents provide heat, minerals, and chemical gradients — all potential energy sources.
- Extremophile microbes found in vents today may resemble early life forms.
- Vents’ stable conditions could protect early life from surface hazards like UV radiation.
- Chemosynthetic bacteria use vent chemicals to produce food without sunlight.
- Fossil and chemical evidence suggests vent ecosystems existed over 3 billion years ago.
🔍 TOK Perspective: How do scientists decide between competing origin hypotheses when direct observation is impossible?
🌐 EE Focus: An EE could analyse genomic evidence of extremophile adaptations to assess whether vent environments are plausible origins of life