D3.3.2 REGULATION OF TEMPERATURE AND BLOOD GLUCOSE
📌Definition Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Thermoregulation | Control of internal body temperature within limits. |
| Vasodilation | Widening of arterioles to increase blood flow to the skin for heat loss. |
| Vasoconstriction | Narrowing of arterioles to conserve heat. |
| Insulin | Hormone secreted by β-cells to lower blood glucose. |
| Glucagon | Hormone secreted by α-cells to increase blood glucose. |
📌Introduction
Temperature and glucose control are prime examples of homeostasis in action. Thermoregulation ensures enzymes function near 37 °C, while glucose regulation provides a constant energy supply. Both involve negative feedback loops, with the hypothalamus and pancreas playing central roles.
📌 Thermoregulation

- Hypothalamus detects core temperature via thermoreceptors.
- Heat loss: vasodilation, sweating, hair flattening.
- Heat conservation: vasoconstriction, shivering, brown fat metabolism.
- Thyroxine modulates metabolic heat production.
- Behavioural responses (seeking shade, clothing) complement physiology.
🧠 Examiner Tip: State that vasodilation/constriction occur in arterioles, not capillaries (a common exam error).
📌 Blood Glucose Regulation
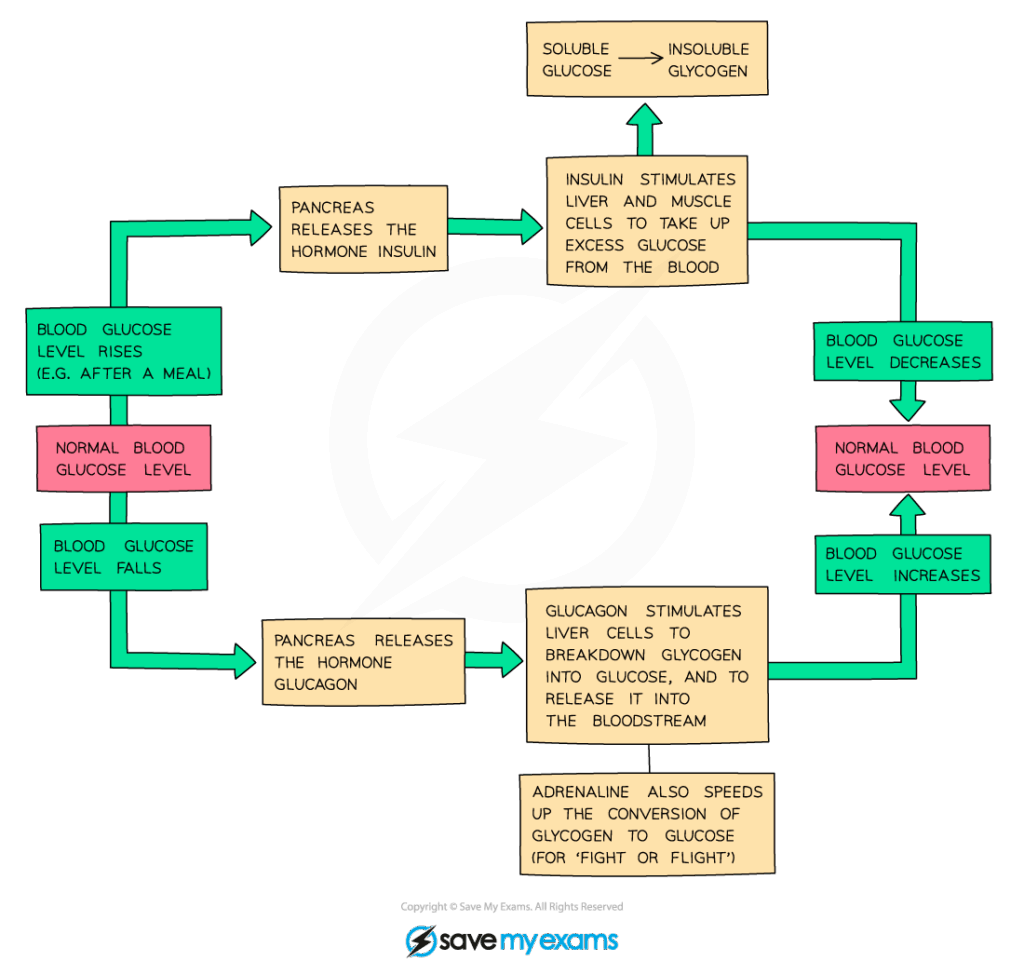
- High glucose → β-cells secrete insulin → uptake by cells, glycogenesis, increased respiration.
- Low glucose → α-cells secrete glucagon → glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, reduced respiration.
- Balance prevents hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
- Type 1 diabetes: lack of insulin production.
- Type 2 diabetes: insulin resistance.
🧬 IA Tips & Guidance: A lab on how exercise affects glucose levels (measured with glucose test strips) links data to regulation.
📌 Integration of Systems
- Endocrine system (pancreas, thyroid) and nervous system coordinate.
- Hormones act on target organs (liver, muscle, adipose tissue).
- Thermoregulation affects metabolic demand for glucose.
- Breakdown of regulation leads to disease (diabetes, heatstroke).
- Illustrates complexity of feedback loops.
🌐 EE Focus: An EE could explore hormonal regulation in diabetes or compare thermoregulation in mammals vs reptiles.
📌 Medical and Social Applications
- Diabetes management: insulin therapy, diet, exercise.
- Fever illustrates deliberate thermoregulation changes in infection.
- Sports medicine relies on glucose and temperature monitoring.
- Thermoregulation strategies crucial for survival in extreme climates.
- Advances in endocrinology have improved quality of life for millions.
❤️ CAS Link: Students could organize a diabetes awareness campaign, demonstrating how lifestyle choices impact glucose regulation.
🌍 Real-World Connection: Temperature and glucose regulation are vital for survival. Failures lead to major diseases (heatstroke, diabetes). Medical interventions—insulin injections, glucose monitors, cooling therapies—show practical applications of homeostatic principles.
📌 Broader Importance
- Links energy metabolism with environmental adaptation.
- Illustrates cooperation of multiple systems.
- Disruption has immediate and long-term consequences.
- Essential for survival in changing climates and diets.
- A classic model of feedback regulation.
🔍 TOK Perspective: Blood glucose and temperature can be measured directly, but the mechanisms (e.g., hormone binding) are inferred. TOK reflection: How do models of unseen processes shape scientific explanations?