D3.2.3 PEDIGREE ANALYSIS AND PROBABILITY
📌Definition Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Pedigree | A diagram showing inheritance patterns across generations in a family. |
| Autosomal dominant | Trait appears in every generation; equal distribution in sexes. |
| Autosomal recessive | Trait may skip generations; carriers exist. |
| Sex-linked trait | Trait carried on sex chromosomes, often showing sex-specific inheritance. |
| Carrier | Individual with one copy of a recessive allele who does not express the trait. |
📌Introduction
Pedigree analysis is used to trace inheritance in families and determine the mode of transmission of genetic traits. Combined with probability, it allows predictions about the likelihood of offspring inheriting certain conditions. This approach is fundamental in medicine, breeding, and genetic counselling.
📌 Pedigree Symbols and Conventions
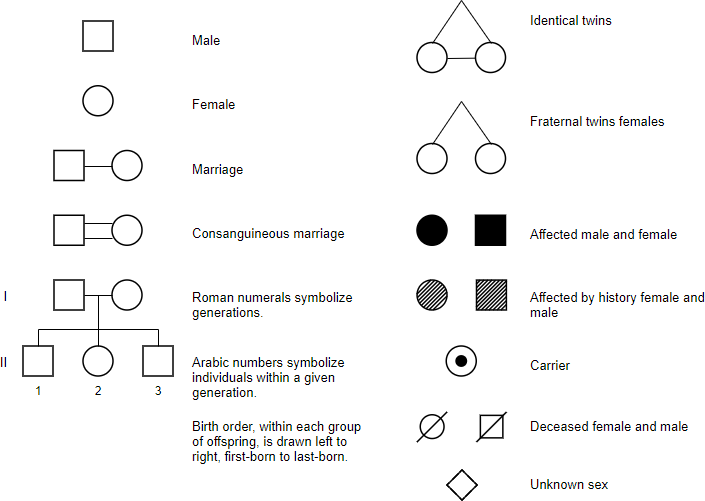
- Squares = males; circles = females.
- Shaded symbols represent affected individuals.
- Horizontal line = mating; vertical lines = offspring.
- Roman numerals = generations; numbers = individuals.
- Carriers may be half-shaded in recessive conditions.
🧠 Examiner Tip: Always indicate whether a pedigree shows dominant, recessive, or sex-linked inheritance, and justify with evidence (e.g., skipping generations or male bias).
📌 Patterns of Inheritance
- Autosomal dominant: affects both sexes equally, appears every generation.
- Autosomal recessive: may skip generations, carriers common.
- X-linked recessive: more males affected, females often carriers.
- X-linked dominant: affects both sexes, but often more severe in males.
- Mitochondrial inheritance: passed from mothers to all offspring.
🧬 IA Tips & Guidance: Students could construct family pedigrees for simple traits (e.g., attached earlobes) and analyze inheritance patterns in their community.
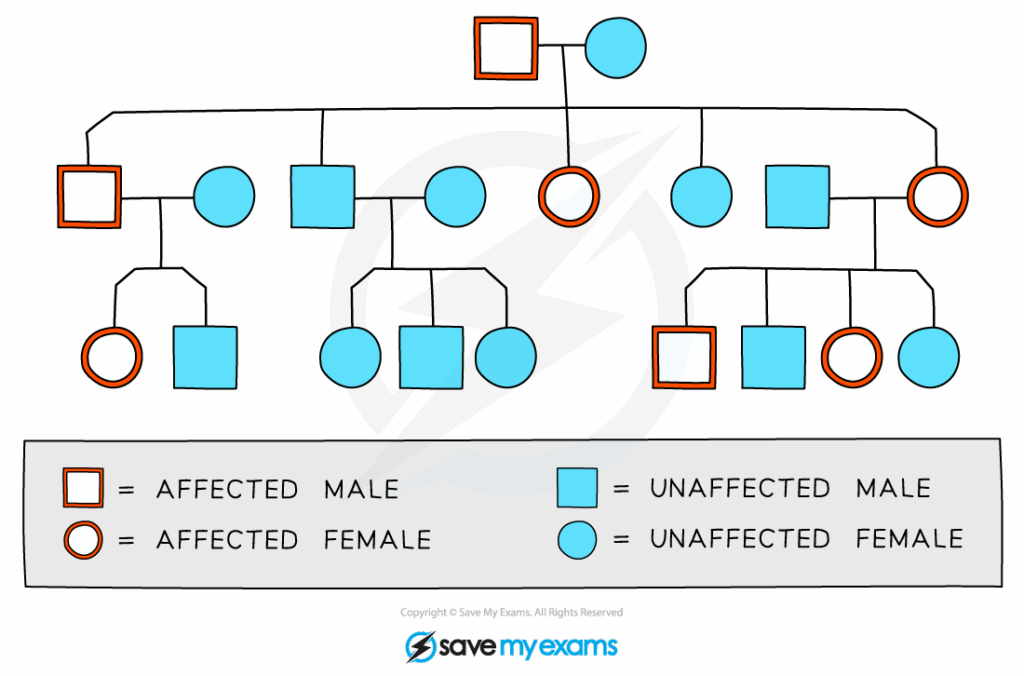
📌 Probability in Genetics
- Probability rules applied to predict inheritance likelihood.
- Multiplication rule: probability of independent events both occurring.
- Addition rule: probability of one event or another occurring.
- Used in predicting carrier status and disease risk.
- Important in population genetics and genetic counselling.
🌐 EE Focus: An EE could investigate the use of probability in predicting inheritance in populations, linking genetics with statistics.
📌 Applications of Pedigree Analysis
- Genetic counselling for families with inherited conditions.
- Identifying carriers of recessive disorders.
- Determining inheritance mode of rare conditions.
- Breeding programs in animals and plants.
- Forensics and ancestry tracing.
❤️ CAS Link: Students could design workshops on reading pedigrees, connecting science with health education in the community.
🌍 Real-World Connection: Pedigree analysis is central in diagnosing genetic disorders like hemophilia and cystic fibrosis. It is widely used in medical counselling, breeding programs, and ancestry testing.
📌 Integration of Probability and Pedigrees
- Provides tools to predict disease likelihood in families.
- Links classical genetics with modern diagnostics.
- Combines statistical reasoning with biological inheritance.
- Enables informed decision-making in medicine and breeding.
- Enhances understanding of genetic risks in populations.
🔍 TOK Perspective: Pedigrees simplify complex inheritance into diagrams. TOK reflection: How does the use of visual models influence our confidence in understanding and communicating scientific knowledge?