A4.2.1 – BIODIVERSITY AND ITS IMPORTANCE
📌Definition Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
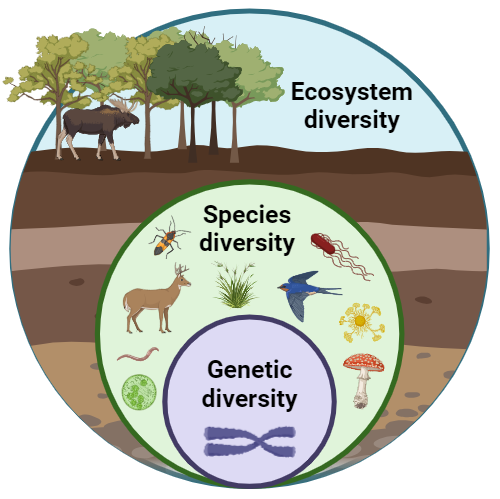
| Biodiversity | The variety of life in all its forms, levels, and combinations, including genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. |
| Genetic Diversity | The variation of genes within a species, providing the raw material for adaptation and evolution. |
| Species Diversity | The number of different species and their relative abundance in an area. |
| Ecosystem Diversity | The variety of ecosystems and ecological processes within the biosphere. |
| Endemic Species | Species found only in a specific geographic location. |
📌Introduction
Biodiversity is the foundation of ecosystem stability, resilience, and productivity. It is essential for maintaining ecological balance and supporting human well-being through ecosystem services such as food production, water purification, climate regulation, and cultural enrichment. Biodiversity exists at multiple levels — from genetic diversity within species to the variety of ecosystems across landscapes — and is the result of millions of years of evolutionary processes. Its preservation is vital for sustaining life on Earth and adapting to environmental changes.
📌 Levels of Biodiversity
- Genetic diversity ensures populations can adapt to changing environments.
- Species diversity maintains ecosystem balance and resilience.
- Ecosystem diversity supports a wide range of ecological processes.
- All levels are interconnected and influence each other.
- Loss at one level often impacts the others.
- Measurement uses indices such as Shannon-Wiener or Simpson’s index.
🧠 Examiner Tip: When describing biodiversity, always specify the level (genetic, species, or ecosystem) and give an example.
📌 Importance to Ecosystem Functioning
- Enhances ecosystem productivity through niche differentiation.
- Increases stability against environmental fluctuations.
- Supports nutrient cycling and energy flow.
- Provides habitat for a variety of organisms.
- Ensures pollination and seed dispersal.
- Promotes resilience to invasive species and disease outbreaks.
🧬 IA Tips & Guidance: An IA could investigate species diversity in different habitats using a quadrat or transect sampling method.
📌 Importance to Humans
- Provisioning services: food, water, raw materials, medicines.
- Regulating services: climate regulation, flood control, disease regulation.
- Cultural services: recreation, spiritual value, education.
- Supporting services: soil formation, primary production.
- Acts as a genetic resource for crop and livestock improvement.
- Provides economic benefits through tourism and ecosystem products.
🌐 EE Focus: An EE could explore the relationship between biodiversity and crop productivity, analysing how species richness affects yields.
📌 Indicator of Environmental Health
- Healthy ecosystems usually have high biodiversity.
- Sudden biodiversity loss signals environmental degradation.
- Bioindicator species can signal changes in ecosystem quality.
- Monitoring biodiversity helps track climate change impacts.
- Protecting biodiversity protects ecosystem services.
- Restoration ecology aims to recover biodiversity in degraded areas.
❤️ CAS Link: A CAS project could involve organising a biodiversity survey in a local park and presenting results to raise community awareness.
📌 Global Biodiversity Patterns
- Biodiversity is highest in tropical regions and decreases toward the poles.
- Hotspots are regions with high species richness and high threat levels.
- Island ecosystems often have high endemism but are vulnerable to disturbances.
- Mountain regions offer diverse microhabitats increasing species diversity.
- Marine biodiversity is concentrated in coral reefs and coastal zones.
- Climate, geography, and evolutionary history shape biodiversity patterns.
🔍 TOK Perspective: Biodiversity valuation involves subjective decisions about which species and ecosystems are most important, reflecting human perspectives and cultural values.
🌍 Real-World Connection:
Biodiversity underpins global food security, climate stability, and sustainable economic growth, making its protection critical for long-term human survival.