D4.1.3 EVIDENCE AND EXAMPLES OF NATURAL SELECTION
📌Definition Table
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
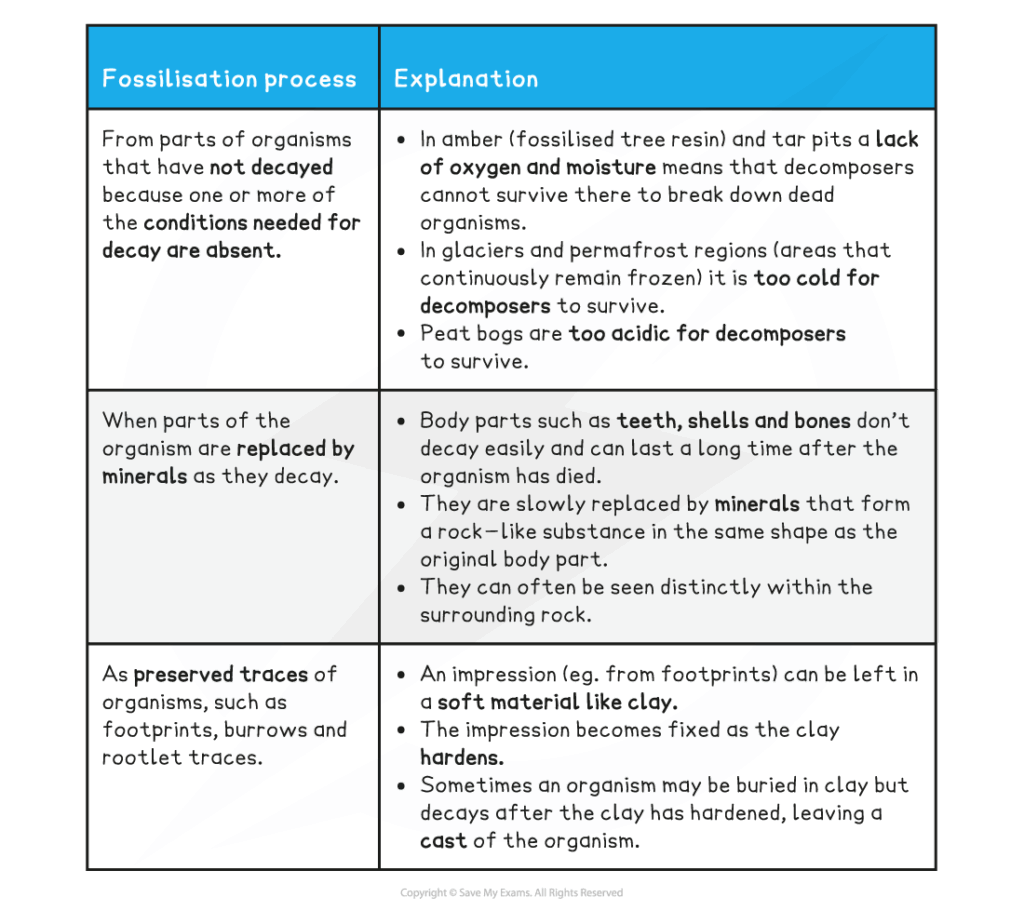
| Fossil record | Preserved remains or traces of organisms showing evolutionary change over time. |
| Homologous structures | Similar structures in different species due to shared ancestry. |
| Analogous structures | Similar functions but different evolutionary origins (convergent evolution). |
| Artificial selection | Human-directed breeding of organisms to emphasise traits. |
| Industrial melanism | Example of natural selection seen in changing frequencies of dark/light moths. |
| Antibiotic resistance | Evolution of bacteria to survive drug treatment, a modern example of selection. |
📌Introduction
Evidence for natural selection comes from multiple disciplines, including paleontology, comparative anatomy, molecular biology, and modern-day observations. Fossils reveal gradual changes, homologous structures show common ancestry, and DNA studies confirm genetic links. Contemporary examples, such as antibiotic resistance in bacteria and pesticide resistance in insects, provide direct evidence of selection in action. Together, these lines of evidence make natural selection one of the most well-supported theories in biology.
📌 Fossil and Anatomical Evidence
- Fossil record shows transitional forms linking ancestors to modern species.
- Homologous structures (e.g., pentadactyl limb) show divergent evolution.
- Vestigial structures (e.g., whale pelvis) indicate evolutionary remnants.
- Analogous structures (e.g., wings in insects vs birds) show convergent evolution.
- Comparative embryology reveals conserved developmental pathways.
🧠 Examiner Tip: Be ready to distinguish homologous vs analogous structures with clear examples — examiners look for precise terminology.
📌 Molecular and Genetic Evidence
- DNA sequencing reveals shared genes among distant species.
- Universal genetic code supports a common ancestor.
- Similar proteins (e.g., cytochrome c) indicate evolutionary relationships.
- Mutation rates in DNA provide molecular clocks for divergence timing.
- Genome analysis reveals horizontal gene transfer in some lineages.
🧬 IA Tips & Guidance: Bioinformatics investigations (BLAST searches, DNA sequence alignments) can be designed to compare homologous genes between species.
📌 Contemporary Examples of Selection
- Peppered moths: shift from light to dark morphs during industrialisation.
- Antibiotic resistance: bacteria evolve mechanisms like enzyme production.
- Insecticide resistance: agricultural pests develop resistance, requiring new controls.
- Climate change: altering selection pressures on migratory and flowering times.
- Experimental evolution: laboratory studies on bacteria show rapid selection.
🌐 EE Focus: An EE could focus on antibiotic resistance as a case study of natural selection under human influence, linking evolution to global health issues.
📌 Artificial vs Natural Selection

- Artificial selection: deliberate breeding for traits (e.g., dogs, crops).
- Mimics natural selection but with humans as selective agent.
- Provides strong evidence for potential of selection to shape traits.
- Risks: reduced genetic diversity, increased vulnerability to disease.
- Natural selection works slower but maintains adaptation to environment.
❤️ CAS Link: Students could create awareness campaigns about antibiotic resistance as a natural selection process accelerated by misuse of drugs.
🌍 Real-World Connection: Understanding natural selection informs conservation, agriculture, and medicine. From breeding resistant crops to designing new antibiotics, it underpins applied biology.
📌 Synthesis of Evidence
- Multiple lines of evidence converge on natural selection as key mechanism.
- Fossils show patterns; molecular biology provides mechanisms.
- Modern examples demonstrate real-time evolution.
- Theory unifies disparate biological observations.
- Makes evolution one of the most robust scientific theories.
🔍 TOK Perspective: Natural selection cannot be observed directly in deep time; it is inferred from multiple indirect evidences. TOK issue: How do scientists establish certainty in theories built on inference rather than direct observation?